Exploring Hyperuricemia
Unraveling the Causes
High uric acid levels, medically termed hyperuricemia, can lead to a multitude of health issues. Dr. Jayant Kumar Hota, a senior consultant in nephrology at Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, sheds light on the various factors contributing to this condition.
The Root Cause: Overproduction and Under-Excretion
Delving into Uric Acid Production
The primary cause of elevated uric acid levels is the body’s inability to regulate its production and excretion properly. Uric acid is a byproduct formed during the breakdown of purines, commonly found in protein-rich foods like red meat, seafood, and certain vegetables.
The Consequences of Imbalance
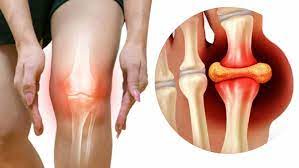
Crystal Formation and Joint Problems
When the body produces excessive uric acid or fails to eliminate it efficiently through the kidneys, the excess uric acid accumulates in the bloodstream. Over time, this can lead to the formation of urate crystals in joints and other tissues, resulting in painful conditions such as gout.
Understanding Contributing Factors
Genetics, Obesity, and Medical Conditions
Several factors can contribute to elevated uric acid levels, including genetic predisposition, obesity, and certain medical conditions like kidney disease, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes. Additionally, certain medications such as diuretics and certain cancer treatments can also elevate uric acid levels.
Prioritizing Prevention and Management
In conclusion, understanding the causes and consequences of high uric acid levels is crucial for maintaining optimal health. By addressing lifestyle factors, managing underlying medical conditions, and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can effectively prevent and manage hyperuricemia and its associated complications.