New Findings on Diabetes Control
Groundbreaking research led by a University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine surgeon-scientist reveals compelling evidence regarding the efficacy of bariatric surgery versus medical and lifestyle modifications in managing type 2 diabetes.
Lead Author Insights
Lead author Anita Courcoulas, M.D., M.P.H., emphasizes the significance of the study’s findings, asserting that bariatric surgery emerges as a safe and potent tool for achieving diabetes control and remission.
Comparative Analysis: Bariatric Surgery vs. Medical Interventions
Methodology Overview
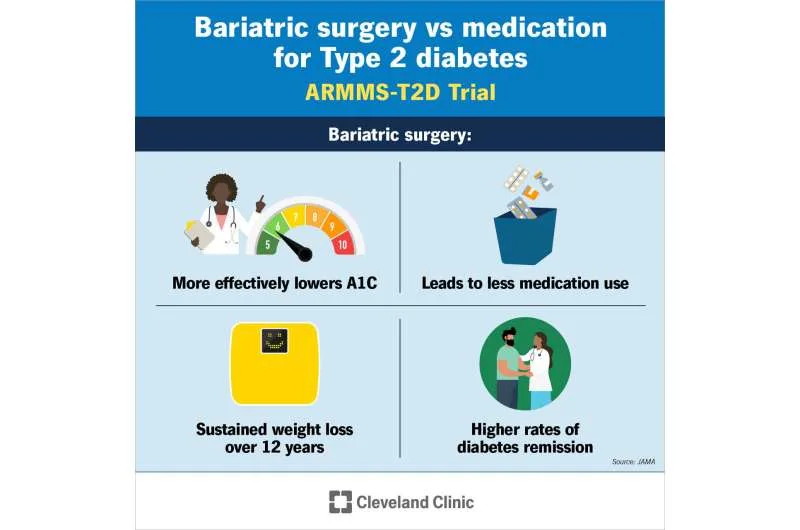
The study compared outcomes of participants enrolled in four separate randomized clinical trials conducted between May 2007 and August 2013. Patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity underwent either bariatric surgery or participated in medical and lifestyle programs.
Key Metrics Analyzed
Researchers scrutinized various parameters, including measures of blood sugar control (HbA1c), weight loss, and insulin and other diabetes medication usage, with long-term outcomes evaluated at seven and 12 years post-randomization.
Superior Diabetes Control with Bariatric Surgery
Participants in the bariatric surgery group consistently exhibited lower HbA1c levels, signifying superior blood sugar control compared to the medical/lifestyle group across all follow-up points.
Remarkable Remission Rates
At year seven, 18.2% of surgery group participants achieved diabetes remission, contrasting with 6.2% in the medical/lifestyle group. By year 12, a stark contrast emerged, with no remissions in the latter group compared to 12.7% in the former.
Durable Weight Loss and Beyond
Sustained Weight Reduction
Bariatric surgery patients sustained an average weight loss of 19.3% at year 12, outperforming the 10.8% achieved by those in the medical/lifestyle intervention group.
Safety and Considerations
While mortality and major cardiovascular events did not differ significantly between groups, adverse effects such as anemia, fractures, and gastrointestinal symptoms were more prevalent among bariatric surgery recipients.
Implications for Diabetes Management
The research underscores the pivotal role of bariatric surgery in achieving long-term type 2 diabetes control and remission. With superior outcomes in blood sugar control, weight loss, and diabetes medication reduction, bariatric surgery emerges as a transformative intervention.