A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This can result in damage to brain cells and potentially permanent neurological impairment. While strokes can be life-threatening and debilitating, many can be prevented through lifestyle changes and proactive measures. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of stroke, including its types, risk factors, symptoms, and crucial precautions individuals can take to minimize their risk.
Types of Stroke
There are three primary types of stroke:
1. Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic strokes occur when a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain becomes blocked or narrowed, reducing blood flow. This is the most common type of stroke, accounting for approximately 87% of all cases.
2. Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a weakened blood vessel in the brain ruptures and leaks blood into the surrounding tissue. This type of stroke is less common but tends to be more severe and often has a higher mortality rate.
3. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Also known as a “mini-stroke,” a TIA is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain, typically lasting for a few minutes to a few hours. While TIAs do not cause permanent brain damage, they are often warning signs of an impending stroke and should be taken seriously.
Risk Factors for Stroke
Several factors can increase an individual’s risk of experiencing a stroke, including:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Family history of stroke or cardiovascular disease
- Age (risk increases with age)
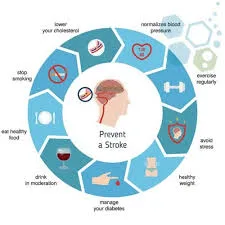
Precautions for Stroke Prevention
While certain risk factors for stroke, such as age and family history, cannot be changed, many can be modified through lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Here are some essential precautions for stroke prevention:
1. Manage High Blood Pressure
Hypertension is the single most important risk factor for stroke. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes (such as a healthy diet and regular exercise) and medications can significantly reduce the risk of stroke.
2. Quit Smoking
Smoking doubles the risk of stroke by damaging blood vessels and increasing the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. Quitting smoking can dramatically reduce stroke risk.
3. Control Diabetes
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of stroke due to elevated blood sugar levels. Proper management of diabetes through medication, diet, and exercise is essential for stroke prevention.
4. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help control weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of stroke.
5. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of stroke.
Stroke is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate attention. By understanding the types, risk factors, and symptoms of stroke, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk and lead healthier lives.