Measles: Symptoms and Causes
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious viral infection characterized by fever, cough, runny nose, sore throat, and a distinctive red rash. It spreads through respiratory droplets and can lead to serious complications, especially in young children, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Recognizing the Signs
– Fever and Rash
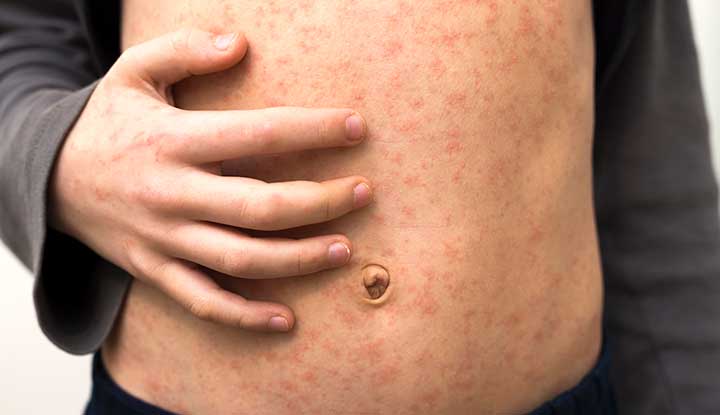
Measles typically begins with a high fever, accompanied by a cough, runny nose, and red, watery eyes. A few days later, a red, blotchy rash appears on the face and spreads down the body, causing discomfort and itching.
Understanding the Transmission
– Contagious Nature
Measles is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus can remain airborne for several hours, making it easy to contract in crowded or enclosed spaces.
Treating Measles: Tips for Recovery
While there is no specific antiviral treatment for measles, supportive care can help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery. Here are some essential tips for managing measles at home:
1. Rest and Hydration
– Importance of Rest
Get plenty of rest to help your body fight off the infection and regain strength. Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, herbal teas, and electrolyte-rich beverages, to stay hydrated and prevent dehydration.
2. Manage Symptoms
– Over-the-Counter Medications
Take over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to reduce fever and relieve discomfort. Avoid aspirin in children and teenagers, as it can increase the risk of a rare but serious condition called Reye’s syndrome.
3. Maintain Respiratory Hygiene
– Preventing Spread
Practice good respiratory hygiene by covering your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing. Dispose of used tissues properly and wash your hands frequently with soap and water to prevent spreading the virus to others.
Prevention: Vaccination is Key
The most effective way to prevent measles is through vaccination. The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is safe, highly effective, and provides long-lasting immunity against the disease. It is recommended for all children and adults who have not been previously vaccinated.
Overcoming Measles with Care
In conclusion, measles is a serious but preventable disease that requires proper management and care. By recognizing the symptoms, seeking medical attention, and following preventive measures such as vaccination, we can effectively combat measles and protect our communities from outbreaks.